If you’re just getting started with Postman API monitoring, we recommend that you read the Postman API monitoring overview article to know its key features and functions.
This article explains how variables are captured from your Postman collection and how you can populate their values for use in the entire API scenario.
Variables
Variables in Postman are used to store and reuse values across different requests, scripts, and environments. They help you manage dynamic data, such as authentication tokens, API keys, or any other value that may change over time or between different environments.
When you import a Postman collection that uses variables like {{VariableName}} in any requests, scripts, or environments, the
Postman API monitor automatically detects and creates these as predefined variables for you. These variables are listed in the Variables section of the monitor editor and you only need to populate their value. This is helpful when you want to easily authenticate with APIs that require a username, password, or secret key.
Use case
Let’s say you imported a Postman collection with an API endpoint: GET {{baseUrl}}/{{secretkey}}/.... This GET request allows you to authenticate from different environments using your secret key as login credentials.
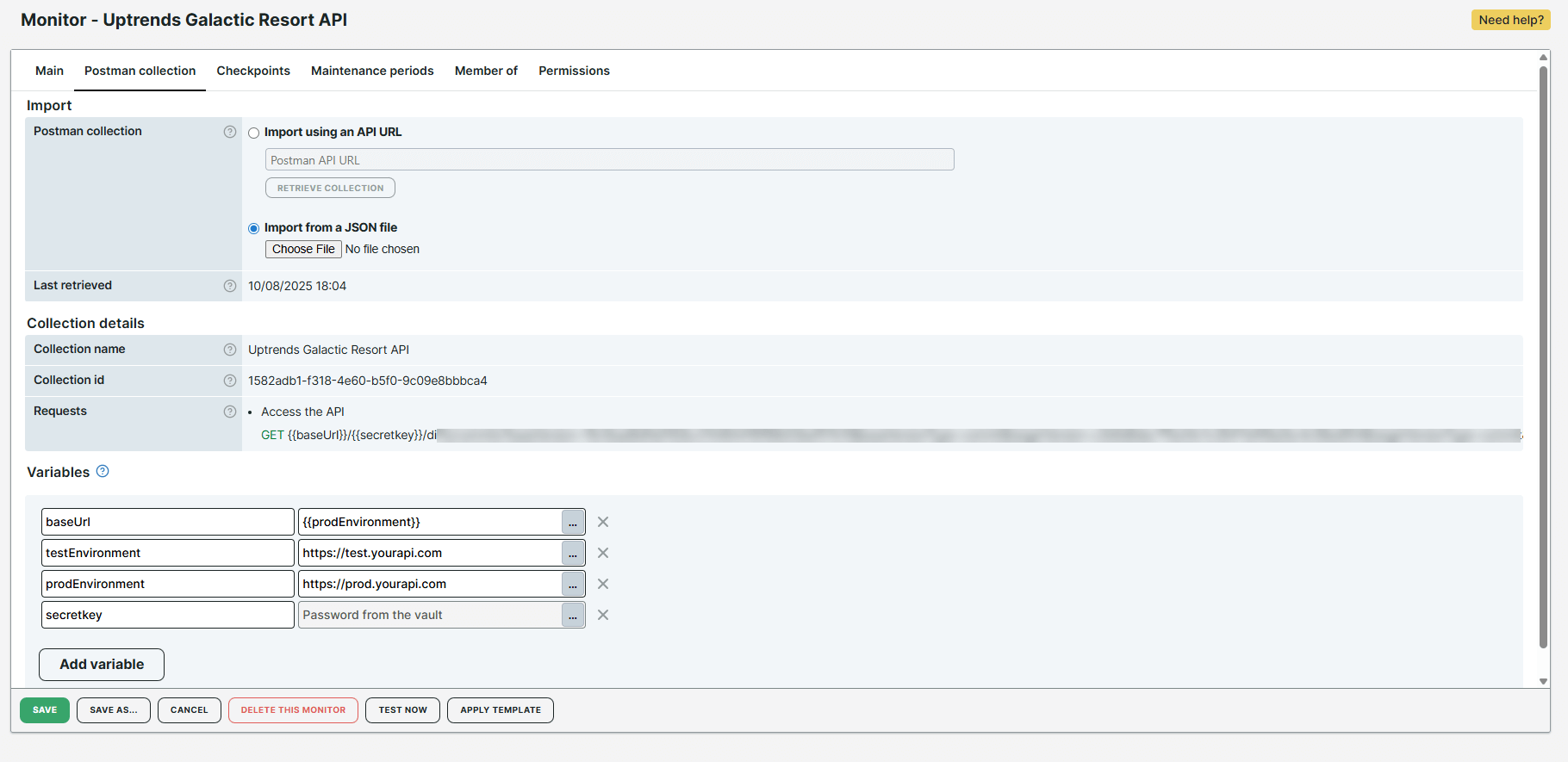
As part of the Requests, the monitor recognizes that two variables, {{baseUrl}} and {{secretkey}}, are defined in your collection. These variables are automatically created and displayed in the Variables of the monitor editor. You can easily populate their values or add more variables based on your monitoring requirements.
As shown in the image, four variables were created: two automatically by the monitor and two defined by you.
- The
prodEnvironmentandtestEnvironmentare user-defined variables that store production and test environment URLs. These are manually added and can be used throughout the entire API scenario using the syntax,{{VariableName}}. - The
baseUrlvariable was automatically generated and identified by the monitor. Its value was set to{{prodEnvironment}}so it can be used in the production environment. If you want to test in the test environment, replace{{prodEnvironment}}with{{testEnvironment}}. This lets you switch between environments quickly without manually modifying your collection or individual requests. - The
secretkeyvariable was automatically generated and identified by the monitor. It contains a value from the Vault, specifically a password from a credential set.
Set up variables
Once you have imported your Postman collection, you can assign values in variables either through plain text or using the Vault.
Assign values to variables using plain text
To assign values to variables using plain text, do the following:
- Go to Variables.
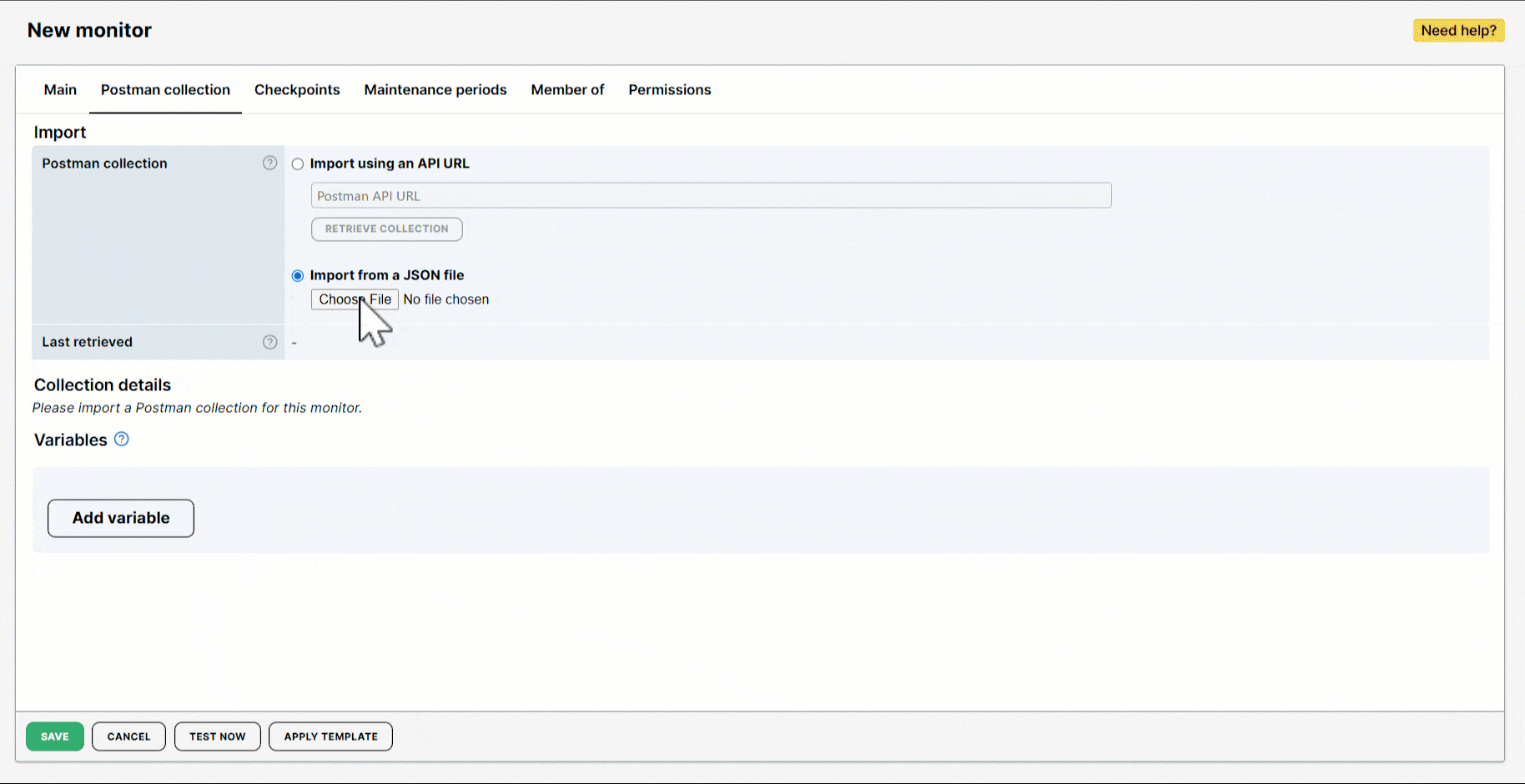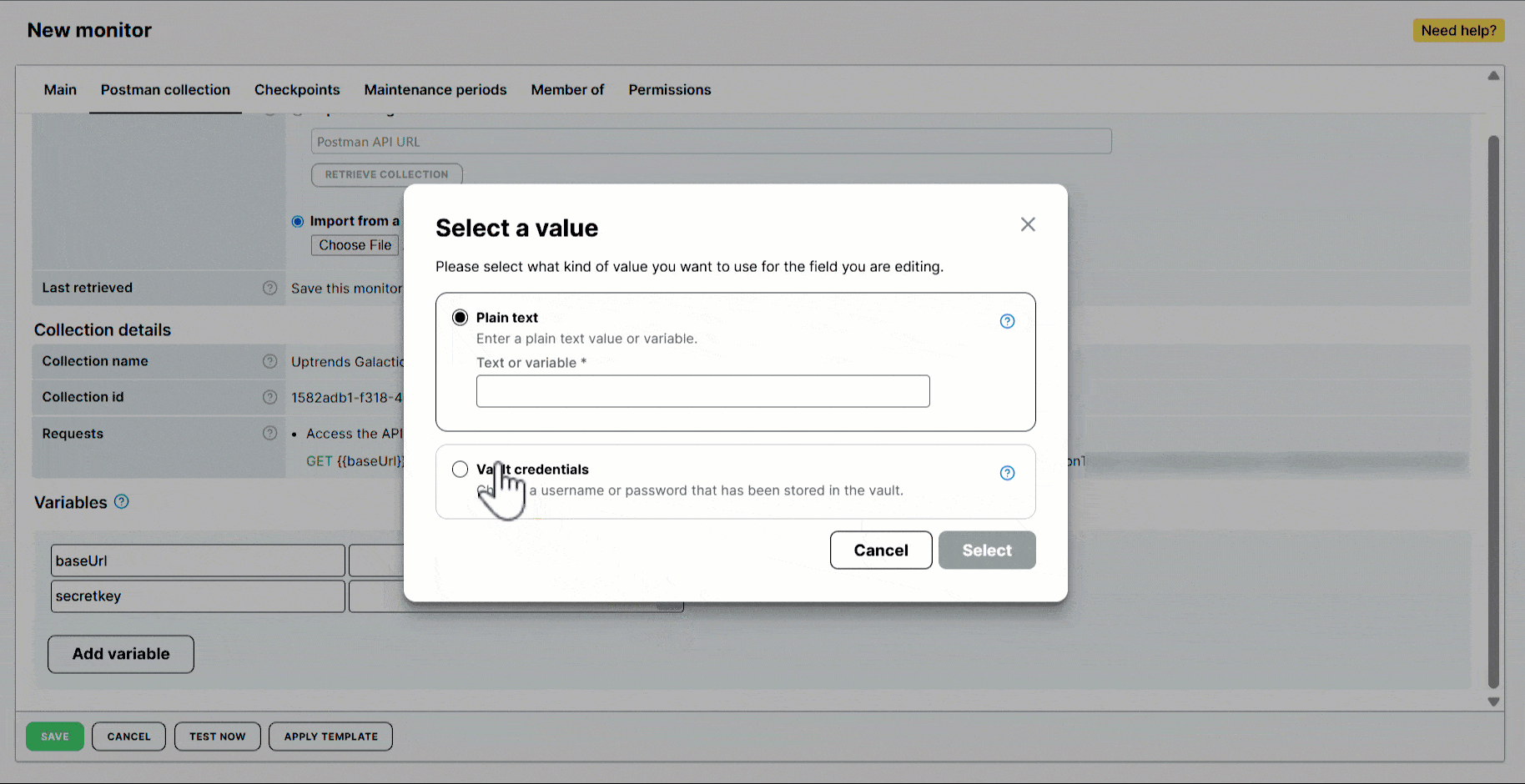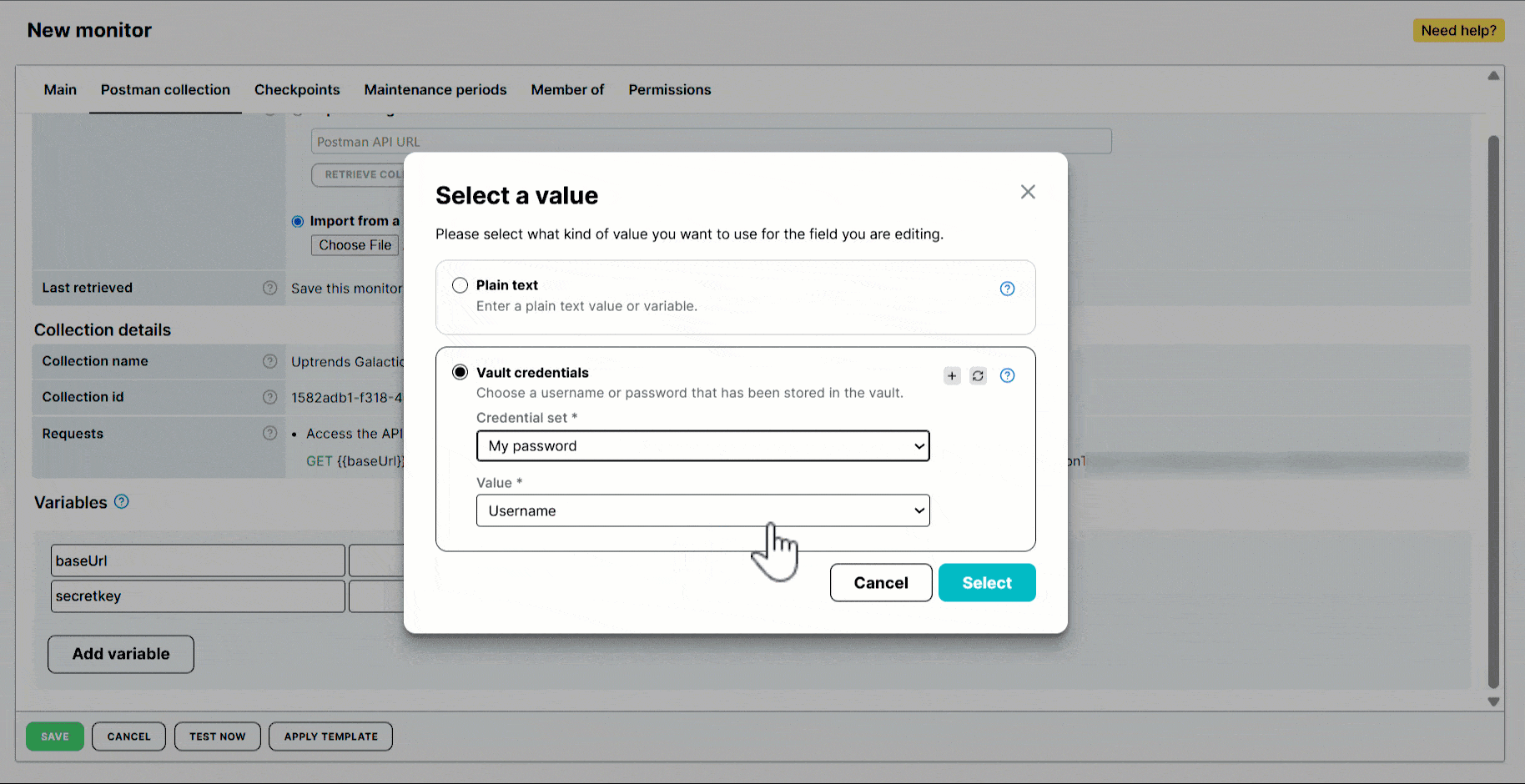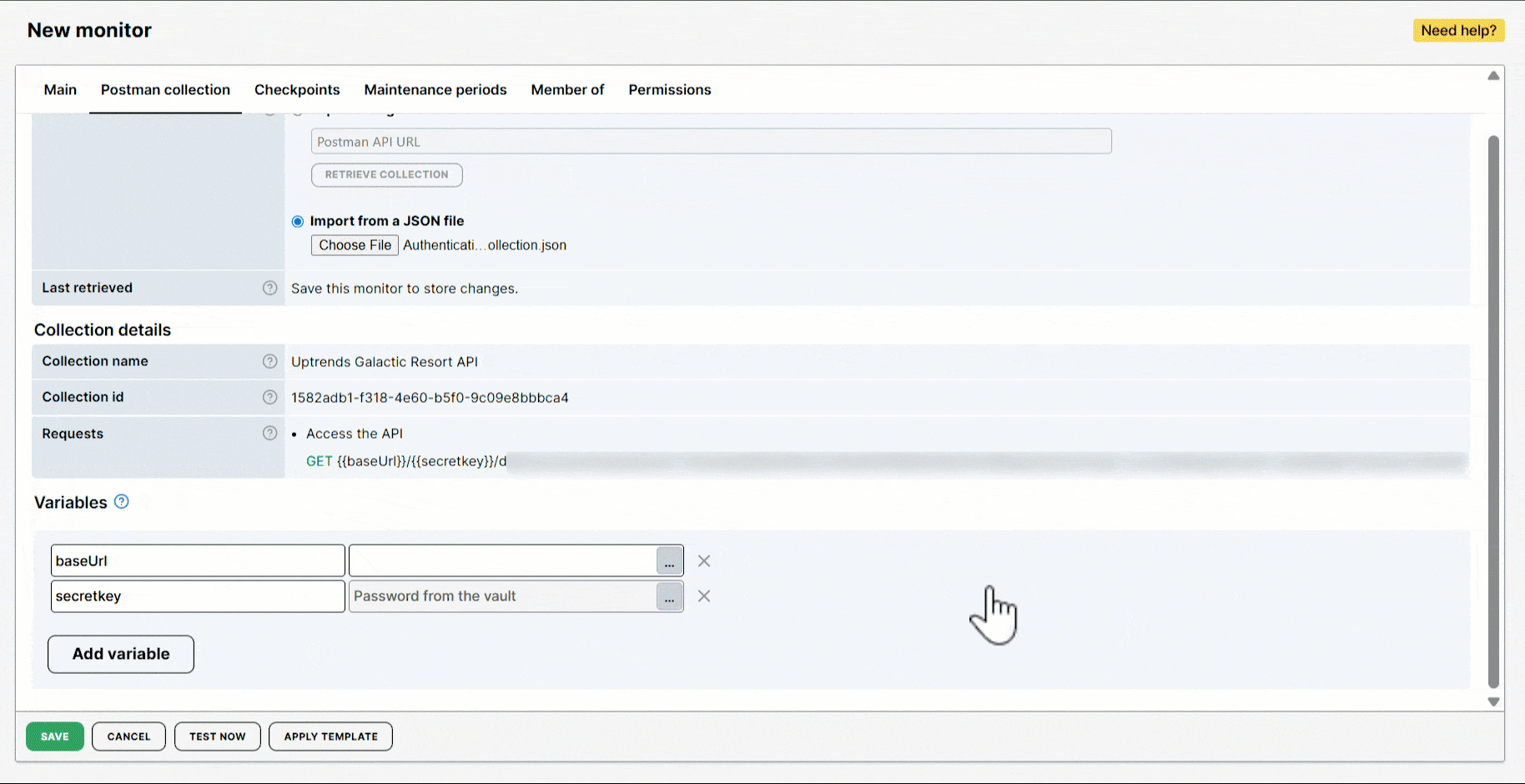
- Identify the variable you want to assign a value to. Click .
- Select Plain text.
- Provide a text or a variable in the Plain text field. For example,
https://test.yourapi.comor{{VariableName}}. - Click Select.
Every time your monitor runs and encounters a variable, it will use the value you provided. If you set the baseUrl to https://test.yourapi.com, the API request will be sent to https://test.yourapi.com/.... If you set the secretkey to {{secretKeyVariable}}, it will use the value of that variable.
Assign values to variables using vault items
Variables can also store vault items, which contain sensitive information from the Uptrends Vault.
To assign values to variables using vault items, do the following:
- Ensure that you’ve added your credentials in the Uptrends Vault.
- Identify the variable you want to assign a value to. Click .
- Select Vault credentials.
- Select a credential set along with its value. For example, select a username or password.
- Click Select.
Every time your monitor runs and encounters a variable, it will use the value you provided. If you use the password from your credential set, the {{secretkey}} will hold the value Password from the vault.